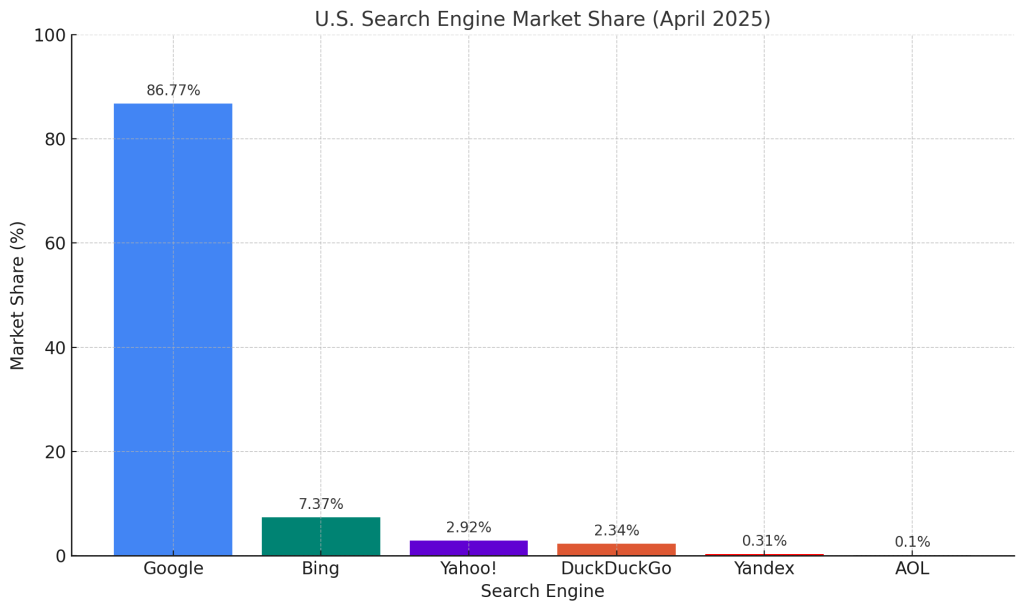
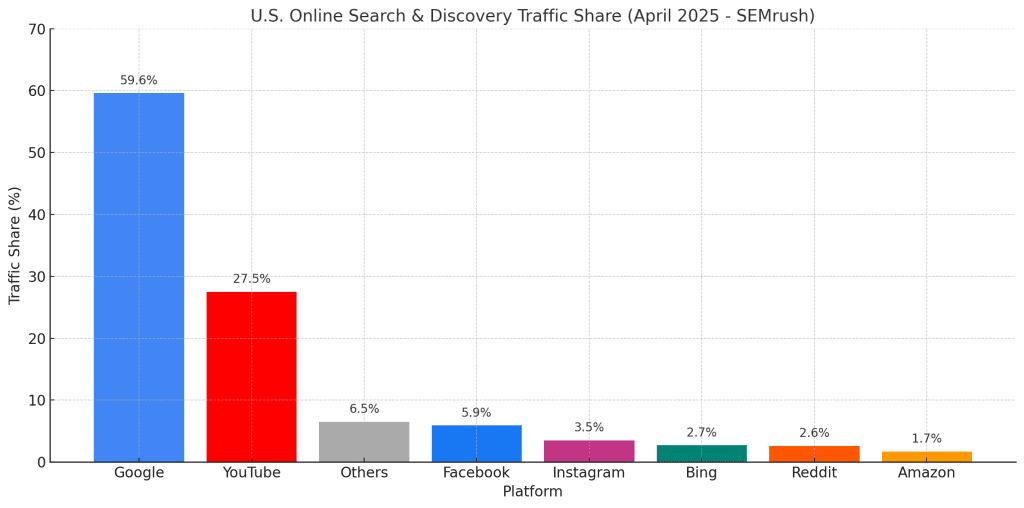
In the world of online commerce, it’s Google’s world, and we just live here. Need proof? Here’s the latest search engine market share as of April 2025.
Of course, that is just search engines. If you look at market share of just people searching for something, Google still reigns supreme with a distant YouTube, Facebook, and Amazon rounding out the top 3. In this scenario, Bing ranks a paltry 4th.
So, as a business who is looking for search to help with sales, how do you get in Google’s good favor? We’ll break it down in simple terms so you can understand the basics — and maybe even improve your own website’s rank.
Understanding Google’s Business Model
The first step to get ranked well on Google (and other search engines) is understanding the products Google actually sells–-reliability, security and accuracy. In fact, it’s so successful at selling those three things that their name has become a barometer of truth. “Google it” is shorthand for “find the answer.” As such, for your website to rank well, it has to be a reliable, secure, and accurate source of content for whatever you want to be known for. Obviously, that is easier said than done. But the more your website helps Google provide reliable results, the more Google will reward you.
How Does Google Decide What Results to Show Searchers?
-
Content Quality
As stated previously, Google’s primary goal is to give people useful answers to their questions. So, it looks at how helpful, accurate, and reliable your content is.
-
-
- Does your page clearly answer the question the searcher asked?
- Is it written by someone who knows the topic or has some sort of authority on the subject?
- Is it original (not copied) content?
- Is it engaging (i.e., Do people link to you? Do people comment on blogs?
-
The better your content, the more likely Google is to rank it higher.
-
Keywords
Speaking of content, keywords are the prize every site is chasing. And there are two types of keywords: the keywords you think you should rank for and the keywords your target audience actually uses to search. For example, if you sold lawn mowers, you might want to be ranked for “zero-turn radius mower” because those are your high-margin products. But you might be better off ranking for “best lawn mower for tight spots” or “mower that turns easy” because that is the vernacular your target audience uses. Always approach search from your customer’s p.o.v.
Now some of you may have heard that Google ranks websites, in-part, by the ‘meta’ tag information on a website page. Unfortunately, this is not true. According to Google’s own blog from 2009, ‘meta’ tags on a website are generally ignored and don’t affect ranking. The ‘meta description’ tag is sometimes used in SERP snippets, but that does affect ranking.
Include keywords in your:
-
-
- Page title
While Google’s response on the actual ranking affect the title tag has on a webpage is murky, it is advised that you include the keyword, naturally of course, in your page title - <H1> and<H2> Headings
Google advises using one <h1> tag per page to clearly define the main topic—this should be your primary headline and include your primary keyword. The <h2> header(s) should contain your secondary keywords. Use <h2>, <h3>, and so on for subheadings to create a clear content hierarchy. Again, the easier you make it for Google to read and understand your page the better it will understand and index your content. - Body text
Google recommends using keywords naturally and strategically to boost rankings, warning against keyword stuffing. Its advanced algorithm understands context and variations, so exact repetition isn’t necessary. - Meta description
Again, although it does not affect ranking, it does provide you with a way to message to people who do find your website through Google. And if you look at SERP snippets as “ad space,” then this is your chance to sell.
- Page title
-
-
User Experience (UX)
Google wants to send people to websites that are easy to use and navigate. For example, all content pieces are identical between two websites, Google will rank the site that sets up that content in a user-friendly way. So, make sure your is website is:
-
-
- mobile-friendly (over 60% of web traffic is mobile)
- loads fast
- is easy to read
- has a low bounce-rate
-
Google’s algorithm uses these indicators, along with Core Web Vitals, to assess the overall user experience. And since its goal is to deliver the most helpful and satisfying results to users, a more user-friendly experience is more likely to earn a top spot in search results.
-
Backlinks
But not all links are equal. Since anyone can have a website, a random link from a random site doesn’t do much good. Remember, Google sells reliability, security and accuracy. A link from a trustworthy site (like a university or news outlet) carries more weight than a link from a random blog. Unless of course, and using the previous example, it was a popular blog on widgets. The Domain Authority of the website sending you traffic is important.
-
Authority and Trust
As we’ve said repeatedly, Google sells reliability, security and accuracy. As such, it tries to figure out how trustworthy and authoritative your site is by checking things like:
-
-
- How long your website has been around – a site a week old may not seem secure to Google
- How many high-quality backlinks you have – remember, it’s quality over quantity
- Does your site use HTTPS? If it doesn’t, you need to add it yesterday. Google asked webmasters several years back to upgrade their sites to HTTPS for a more secure web.
- Is content on your website regularly updated? A website built ten years ago and then never touched, no matter how well constructed, will rank poorly. Consider have a News section or blog to add fresh content.
-
The more established and reliable your site appears, the better your rankings.
-
Location
Google often considers your location to show the most relevant results. For instance, if you search “pizza near me,” it will show local restaurants, not ones across the country.
So if you run a local business, make sure you list your location clearly and set up a Google Business Profile.
What You Can Do to Improve Your Rankings
Going back to our original premise, it’s Google’s world, and we just live in it. Their ranking algorithm uses so many points of reference that it would be impossible to try and keep up with each new iteration and figure them all out. Instead, we recommend you follow these simple tips to improve your own site’s SEO (Search Engine Optimization):
-
- Write helpful, clear, and original content
- Use keywords your audience is actually searching for
- Make your website fast and mobile-friendly
- Earn links from other trustworthy websites
- Update your content regularly
- Create a Google Business Profile if you have a local business
Reliability, Security and Accuracy – It’s All You Really Need.
Google’s ranking system may sound complicated, but at its core, it’s just trying to provide the best answer for one question: “What’s the best page to show the person searching?”
Don’t worry about what the new search algorithm considers important. Just be clear, helpful, trustworthy, and easy to use, and Google will notice — and reward you with better rankings. And one last caveat: Remember, SEO is not instant. It takes time to build trust with Google, but the results are worth it. Higher rankings lead to more traffic, more customers, and more growth.
Want help optimizing your website? Reach out — we’d be happy to help!